In European political institutions, what are women in charge of? How many are in key positions? How many are in decision making roles? Out of the 28 EU members states, only two are lead by women: Germany and Poland.
While Angela Merkel is widely seen as one of the most powerful and influential politicians in the world, very few women can say the same. Openpolis, in its recent MiniDossier “Trova l’intrusa“, analyzed the role of women in political institutions across Europe and Italy. The goal was to understand how many women hold key political positions: what are women in charge of? How many are in key positions? How many are in decision making roles?
The results were very clear. The number of women in political institutions is still very low, and very few of them hold positions of power.
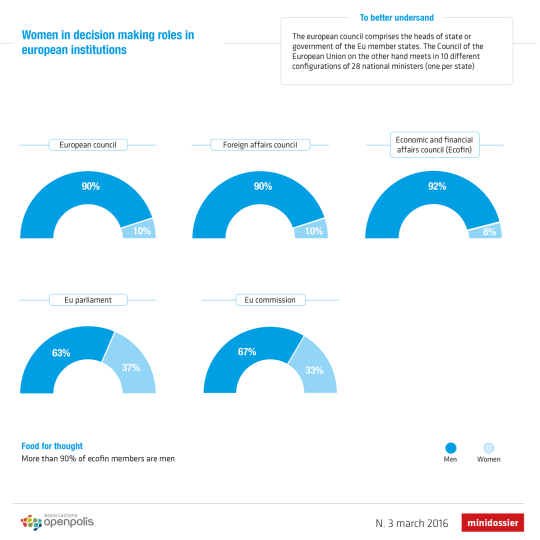
Even though women represent more than a third of members both in the European parliament and in the European commission (37% and 33%, respectively), both in the European Council and the Foreign Affairs Council the percentage drops to 10%. In the most important economic and financial institution of the old continent, Ecofin (Economic and Financial Affairs Council), only 8% of members are women.
In national parliaments of EU members states, men are always the majority (in best of circumstances, Sweden, women reach 44%), in 17 countries the percentage is lower than 30%, and in the governments of three countries (Greece, Slovakia and Hungary) all ministers are men. There are only three countries in which the government is half men and half women: France and Slovenia (both at 50%) and Sweden (52%). Furthermore, of the 5 women heads of state, two are so for house laws (queen Elizabeth II and Margaret II). If we consider only the heads of government, the only female colleague of Angela Merkel, is the Polish premier Beata Szydło.
In national governments, women hold 50% of labour and social affairs ministries, 43% of ministries related to family care, youth, senior citizens and sport, 40% of education and culture. At the same time, only 14% of justice ministers are women, percentage drops to 11% for finance ministries and to 7% for foreign affairs ministries. No EU country has a woman leading the ministry of economy.